Do you exactly understand what the Claim Settlement Ratio in Insurance is?
A lot of people just look at the claim settlement ratio and make an opinion about an insurance company. In this article, let me break some myths and help you understand more about the claim settlement ratio.
What is Claim Settlement Ratio?
In simple words, the claim settlement ratio is the percentage of claims paid in a financial year.
Claim Settlement Ratio = (No of Claim Paid / No of Claims Received)
So if a company gets 1000 claims in a year and pays 985 of them, then its claim settlement ratio for that year will be 98.5%. An important point to note here is that it’s about the number of claims and not the number of claims.
What type of Claims is considered in the Claim Settlement Ratio?
Generally, most of the people willing to buy a term plan look for this ratio as they are concerned about the claim getting paid in case of their early death. But claim settlement ratio is not the same as the “death claim settlement ratio”
In the calculation of the claim settlement ratio (in the case of life insurers), all types of claims are considered like.
- Death Claim: The claims once the policyholder dies
- Maturity Claims: Policies that are maturing and needs to be settled
- Surrender Claims: Policies that are closed prematurely and surrendered
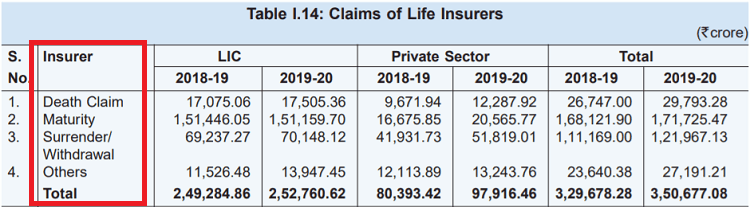
Here is the breakup from the IRDA report of 2019-2020, where you can see the number of claims for LIC and private insurers
Is Claim Settlement Ratio a probability?
One of the biggest myths about CSR (Claim settlement ratio) is that it’s a probability of claim settlement. This is not true and often leads to misjudgment of an insurance company.
CSR is simply a way of representing the data and nothing else. It does not tell you about the intention of the company. Let me share this with an analogy
Imagine there are two VISA processing counters which are looking at documents of people and giving the VISA or rejecting it.
Now if the Visa will be approved or rejected depends mainly on how proper are the documents and the person and not depend on the person who is processing the Visa. If the documents and case fall into the rules set, then it will be approved, else it will not.
So imagine there are two counters A and B . Counter A rejects 5 people out of 100 and Counter B rejects 7 people out of 100.
Now, this simply means that counter A got 5 people who did not fit into the set rules or their documents had issues. In the same way counter, B got 7 people who had incomplete documents.
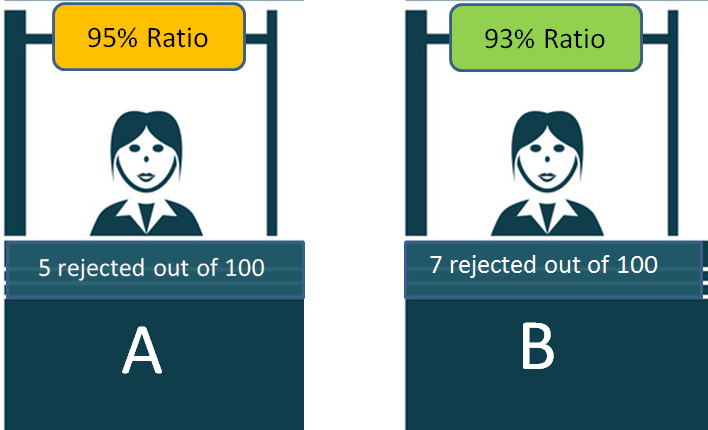
One cannot mistake these 93% (A) and 95% (B) as the probability of their visa getting rejected.
Hence, in the same way, the claim settlement ratio just tells you about what kind of claims did the insurance company received and how many of those claims were rejected. It’s not a probability.
Investors mostly have a very bad view of companies and attribute these rejections to their intentions, which is not a correct way to look at this ratio.
Does Claim Settlement Ratio depend on the policyholder?
Yes
A claim that will be rejected or accepted depends mostly on the policyholder itself. There are many people who file a claim which is bound to get rejected as it’s not valid as per the terms and conditions of the policy document.
Many policyholders also have a very vague and wrong impression of what is covered and what is not. They file claims based on flimsy assumptions and for things that are out of the scope of rules.
Let me give you an example.
Imagine a person who lied to the company while taking a term/health insurance, that he is a smoker and also went through some surgery in past. He lied to the company.
After some years the claim was filed (person died or got hospitalized) and now the company finds out the information provided by the insured person was false and hence the claim should not be paid in this case and it’s totally valid rejection.
So here it’s not the company who had the wrong intention but the customer who created a situation that led to claim rejection. Most of the policies which are rejected fall into this category.
From your end, you have to understand one thing. If you have bought your policy properly and revealed all the information properly, your claim will not be rejected. However, if you give reasons for the company to reject your claims, it will surely be rejected and there is nothing wrong with that.
What is Claim Intimation Ratio?
Claim Settlement Ratio tells you about “number of policies”, whereas Claim Intimation Ratio tells you about the “AMOUNT”
It tells you what percentage of the claim amount was paid out of the total claim amount which was claimed in a year.
Claim Intimation Ratio = (Amount Paid / Total Claim Amount)
Most people are not aware of this ratio, and this gives you better clarity about the claims paid by a company. It may happen that a company has a high claim settlement ratio, but its claim intimation ratio is lower than the other company.
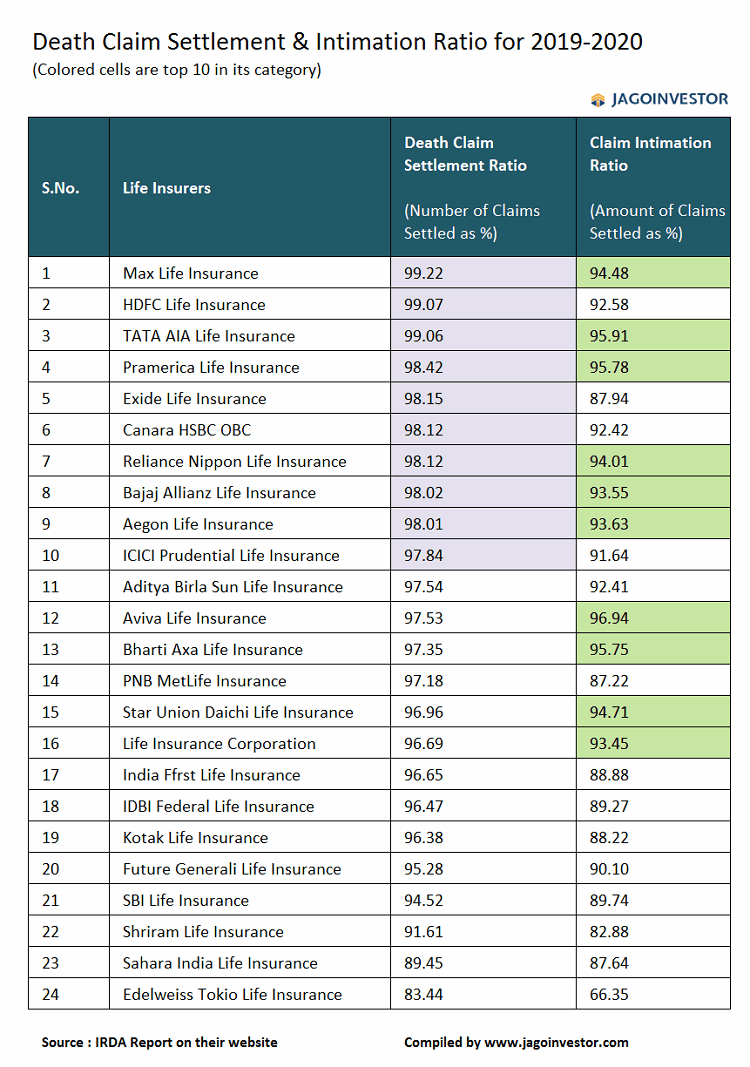
Here is an example of how the Claim settlement ratio can be high despite a low intimation ratio
Company A and B receives 10 claims in a year as follows
- 9 claims of Rs 10 lacs each
- 1 claim of 1.1 crore
[su_table responsive=”yes”]
| Company A | Company B | |
|---|---|---|
| Claim Rejected | 1 claim of 1.1 crores is rejected | 2 claims of 10 lacs are rejected |
| Claim Settlement Ratio | 9/10 = 90% | 8/10 = 80% |
| Claim Intimation Ratio | 90 lacs / 2 crores = 45% | 1.8 crore / 2 crore = 90% |
| Comment | Claim settlement ratio is high, but not the amount paid | Claim settlement ratio is low, but the higher amount paid |
[/su_table]
Business Model of an insurance company
As a customer, you should be very clear about the business model of an insurance company. An insurance company is a for-profit organization whose intention is to stay profitable and work for its profitability and also serve its customers as well.
The insurance company collects a small premium from a large number of people, but that money eventually goes only to a handful number of people who file for a claim. So in a way, it’s a shared resource which is given to those who are valid claimants.
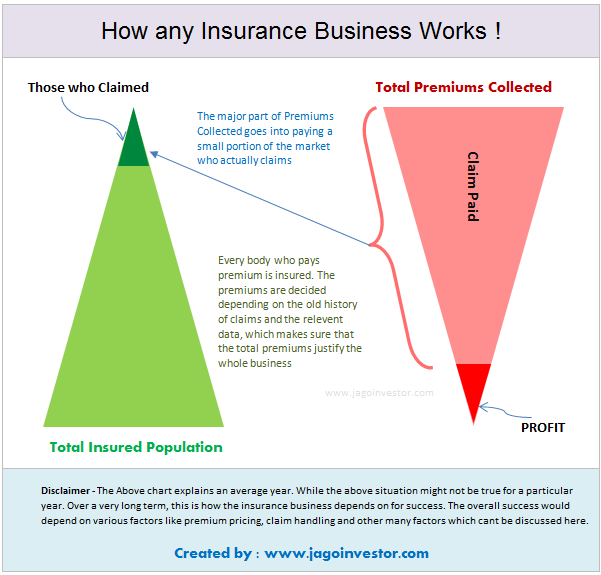
In order to stay in business and be profitable, an insurance company has to reject all the claims which are not valid. If they start paying each and every claim without proper verification, they just won’t survive and it’s not in the customer’s interest.
This simply means that a company with not the best claim settlement ratio, in reality, is a good company because knows how to protect itself and not let a fraudster make a wrong claim.
A very important point to note is that a new insurance company will mostly be getting death claims in the starting 8-10 yrs and not any maturity claims which means their claim settlement ratio may look on the lower side.
How to buy an insurance policy?
Basically here is a high-level step by step process
- Look at a company whose name you trust
- Choose a company which has been few years old (this depends on you)
- Choose a company whose product you like (features etc)
- Check out the experience of other investors online about the company
- Buy a policy with full honesty and by disclosing all information
Don’t lose your sleep over Claim Settlement Ratio
In the end, I just want to say that the claim settlement ratio is not a useful metric for any purpose and you should not lose your sleep over it. Don’t worry too much.