Have you ever asked what is the MRP of a stock ? I don’t think so !
The reason many investors shy away from investing in stock markets is because it seems to be a gamble. With the markets fluctuating every day, dropping or rising at the slightest bit of concern or euphoria, one is bound to be wary of putting one’s hard-earned money here.
And most of us experienced the worst of this volatility during the market crash in 2008; some of us are still recovering from its aftermath. So, how can we ensure that there won’t be a repeat of this scenario? How do we ensure that we do not lose our shirt at the market and make our hard earned money grow into wealth?
We all know that it is important to invest in fundamentally strong companies.
But what is equally important, if not more, is to invest at the right price. But how do we find out the right price for stocks?
Whenever we shop for anything, we are guided by a MRP tag on the wrapper or pack. Unfortunately, we do not have such a MRP tag to guide us when we buy stocks, do we? Well, now you can even have a MRP tag for stocks!
Stocks@MRP can be a great tool for investors to make sensible buy and sell decisions based on fundamentals and not on market sentiments. MoneyWorks4me, have labelled stocks with a MRP tag; something which each one of us can understand and relate to.
What is Stock@MRP based on ?
This price tag for stocks is based on the factor which primarily drives the price of a stock in the long-term – the earnings power of a company. The concept of MRP is based on the fact that, while in the short term, stocks might be affected due to news, sentiments, FII movements etc. over the Long term, the market will invariably reflect a stock’s intrinsic value based on its earnings.
MRP is a tool which helps you to gauge whether the market is under reacting or over reacting to these. As sensible investors, we would be well served if we bought stocks at a considerable discount (ideally 50%) to their MRP and sold off stocks if they are priced considerably above their MRP.
To verify whether this method could have worked well during different time periods, good times as well as bad times, we back tested it for the period 1999-2010 and found that the results are quite gratifying.
Let’s understand this concept with the example of Wipro.
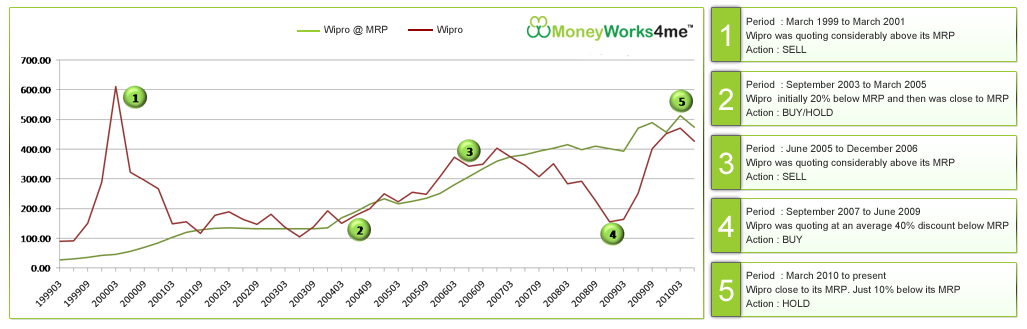
The graph below shows two lines. The Red line is Wipro’s actual stock price for the period 1999 to 2010, whereas the green line is Wipro’s MRP for the same period as calculated by us based on its fundamentals.
The graph shows that Wipro was considerably overvalued for the period 1999-2001 during the Tech bubble. The company was quoting great numbers with a 60% growth in earnings (9 year CAGR growth rate) from 1990 to 2000. Add to it the euphoria of anything related to the IT industry during this period and you see Wipro quoting at as high as 400 times its earnings.
On the other hand, the MRP offers a better view on the intrinsic value of the stock based on its earnings. Not surprisingly then, as the bubble burst the price rocketed down and reached its MRP. From 2001 onwards, Wipro’s price remained close to its MRP, thus indicating that the stock was more or less fairly valued.
Wipro quoted above its MRP values from March 2005 to December 2006.
In March 2006, it was trading at as much as 30% above its MRP. Thus, it is evident that the market was expecting above average earnings in the next few quarters; a difficult thing to achieve continuously.
The EPS for the company grew at an average of around 8% during this period on a Q-o-Q basis. This was a good time to sell the stock as the price rise was not supplemented by a huge rise in earnings.
However, things started turning south for the company post december 2006 with the PE contracting. The company registered a Q-o-Q drop in EPS in June 2007 and it seems the market over reacted to this with the price reaching as much as 20% below the MRP. The company’s earnings registered a drop, again, in June 2008.
Also, after reaching a peak in January 2008, the Sensex started plummeting with the fear of a global economic recession on the cards. Wipro was available at a discount of as much as 60% in December 2008 and March 2009; a clear buy indication.
Within 2 quarters the price of Wipro reached close to its MRP giving an investor, returns of around 50%. Today Wipro is quoting at around 10% discount to its MRP and therefore one should wait for it to come to lower levels to enter. (Read Nifty PE analysis)
Margin of safety
We all know about great value investors like Benjamin Graham and Warren Buffet, who insisted on always buying stocks with a margin of safety. However, it becomes difficult to confidently ascertain what the intrinsic value of a stock is and hence we end up paying a premium for a stock instead of buying it with a margin of safety.
Stocks@MRP helps you to ascertain the intrinsic value of stocks thus ensuring that you always buy stocks which are at a discount to the MRP. As seen in the case of Wipro, following this strategy would have yielded great returns and that too at minimal risk .
Outlook Profit magazine has published a special story on this concept titled “The Right Price” in their issue dated 9th July 2010. The concept can prove to be a very useful tool for investors, enabling them to enter stocks at bargain levels and exit when things start getting over-exuberant!
You can read more about this concept on our blog Stock Shastra. In the subsequent post, we will see how this concept can be extended even to the benchmark index Sensex. We will also take a look at a few stocks which are trading considerably above or below their MRP.
This is the first of a series of guest posts by Nikhil Kale from MoneyWorks4me.com.